Monitoring climate change in the sub-Arctic
Written on June 10th, 2020 by Bilgenur Baloglu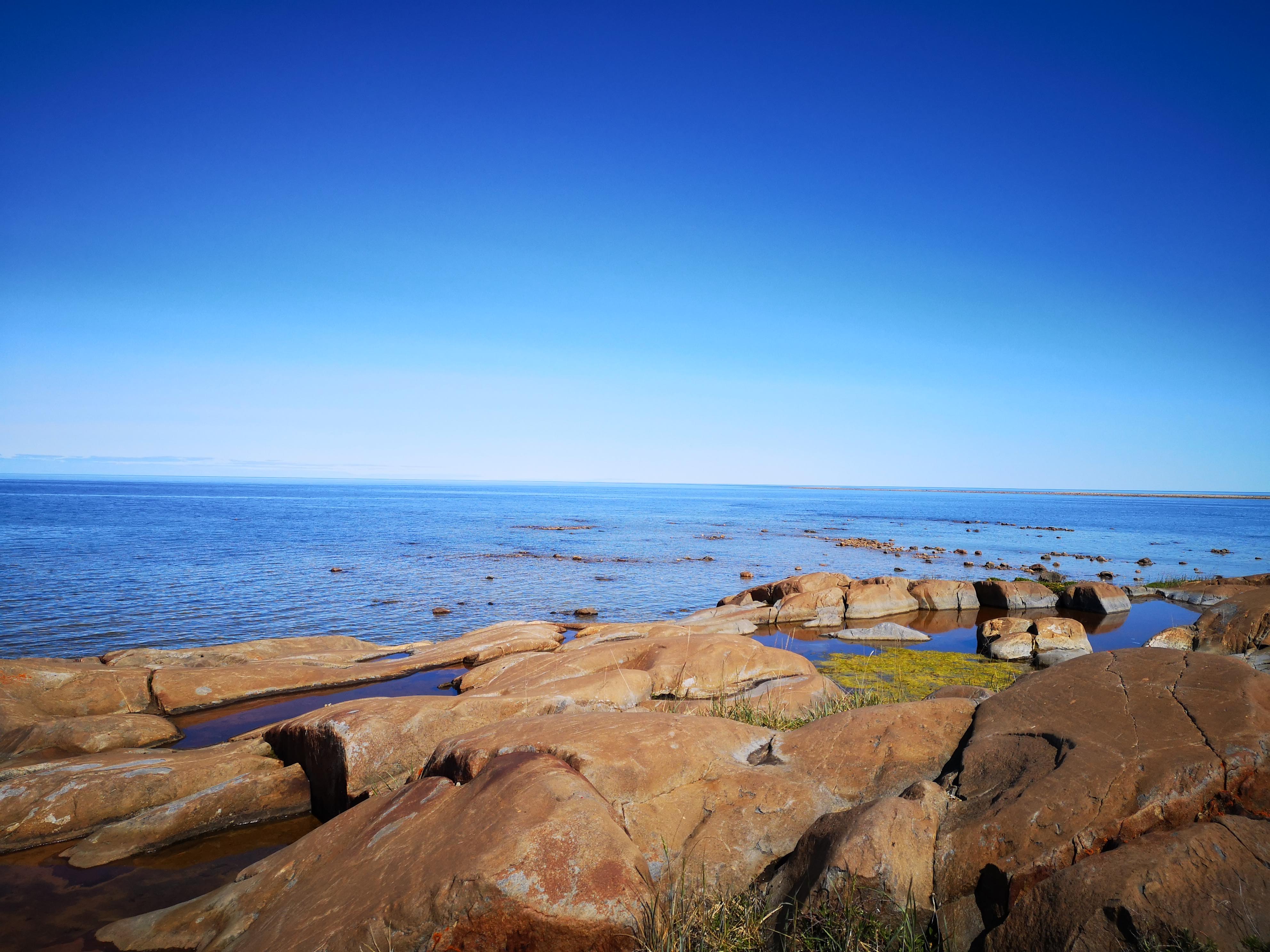
Assessing the effects of climate change on the sub-Arctic midges
We collected chironomid larvae from the microhabitats in tundra ponds and rock bluff ponds by the Hudson Bay. We also collected ecological data. We are interested in understanding what shapes the chironomid communities in each microhabitat in each pond, how the community composition differs between different habitats, and if the speciation patterns are different in microhabitats.
Assessing the current diversity and distribution of chironomids in the Arctic is becoming increasingly important in the face of the climate crisis, given their distribution is expected to change with increased warming and precipitation in polar regions. This assessment will provide a basis for future monitoring of population shifts but it will also by means of comparison with earlier data allow a first peak into the effects of a changing climate within a decade. As the life cycle of chironomids is temperature-dependent, their distributions are very likely to change with increased warming periods.
This project got awarded by Northern Research Fund (NRF) 2019 and sponsored through the Centre for Biodiversity Genomics (CBG). I am the PI in this project. Manuscript in progress.